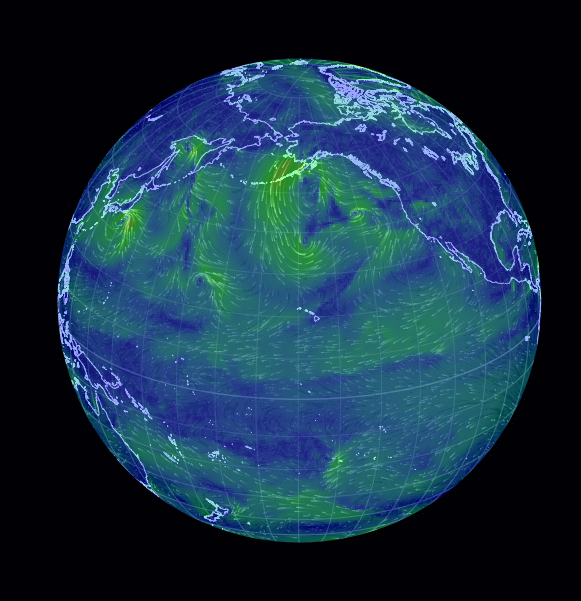
Earth Null is a powerful tool that has transformed the way we visualize and analyze geographic data. With its user-friendly interface and extensive features, Earth Null allows users to interact with complex datasets in a simple and intuitive manner. In this article, we will explore what Earth Null is, its key features, and how it can benefit researchers, educators, and anyone interested in geography.
The importance of geographic data cannot be overstated, especially in a world where information is crucial for decision-making. Earth Null serves as a vital resource for visualizing this data, making it accessible to a wide audience. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will uncover the various applications of Earth Null and how it stands out from other geographic tools available today.
In addition to its ease of use, Earth Null is built on a foundation of trustworthiness and authority, making it a go-to resource for professionals in the field. This article will provide an in-depth overview of Earth Null, including its functionalities, its impact, and tips for maximizing its use.
Table of Contents
- What is Earth Null?
- Key Features of Earth Null
- Applications of Earth Null
- Benefits of Using Earth Null
- Getting Started with Earth Null
- Data Sources and Reliability
- Limitations of Earth Null
- Conclusion
What is Earth Null?
Earth Null, often referred to as Earth Nullschool, is an interactive visualization tool that allows users to explore various global datasets in a 3D format. It utilizes WebGL technology to render data such as wind patterns, ocean currents, and temperature variations in real-time. This platform offers a unique perspective on how different elements of our planet interact with one another.
History of Earth Null
Earth Null was created by Cameron Beccario and has gained significant popularity since its launch. Initially focused on wind patterns, it has since expanded to include a wide range of environmental data. The platform has become a vital resource for scientists, meteorologists, educators, and the general public.
Data Visualization Techniques
The tool employs various visualization techniques to present complex data in a comprehensible manner. Users can manipulate the globe to view specific regions, zoom in and out, and adjust parameters to focus on particular datasets. This interactivity enhances the understanding of geographical phenomena.
Key Features of Earth Null
- Real-Time Data: Earth Null provides real-time updates on various environmental factors, allowing users to observe changes as they occur.
- Interactive Globe: The 3D globe interface allows for seamless navigation and exploration of global data.
- Customizable Layers: Users can select different data layers to visualize specific information.
- Educational Resources: Earth Null offers resources for educators to integrate geographic data into their curricula.
Applications of Earth Null
Earth Null has a multitude of applications across various fields, including:
- Meteorology: Meteorologists use Earth Null to track weather patterns and analyze atmospheric data.
- Environmental Research: Researchers can study the effects of climate change by visualizing temperature and wind patterns.
- Education: Teachers can utilize Earth Null to enhance geography lessons and engage students in interactive learning.
- Disaster Management: The tool aids in disaster preparedness by providing real-time data on natural events.
Benefits of Using Earth Null
Utilizing Earth Null offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Understanding: The interactive format helps users grasp complex geographic concepts more easily.
- Accessibility: Earth Null is available online, making it accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
- Community Engagement: The platform fosters a community of users who share insights and findings.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Organizations can leverage the data visualized by Earth Null to inform their strategies.
Getting Started with Earth Null
To get started with Earth Null, follow these simple steps:
- Visit the official Earth Null website.
- Familiarize yourself with the interface and available datasets.
- Experiment with the interactive globe by zooming in and out and adjusting data layers.
- Explore educational resources and tutorials to maximize your usage of the platform.
Data Sources and Reliability
Earth Null aggregates data from various reliable sources, including:
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF)
- Global Forecast System (GFS)
This ensures that the information presented is accurate and up-to-date, reinforcing the platform's authority and trustworthiness.
Limitations of Earth Null
While Earth Null is a powerful tool, it does have some limitations, including:
- Data Gaps: Some regions may have less available data than others.
- Complexity for Beginners: New users may find the interface overwhelming at first.
- Internet Dependency: The platform requires a stable internet connection to function effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Earth Null is an invaluable resource for anyone interested in geographic data. Its interactive features and real-time updates make it a go-to tool for researchers, educators, and the general public alike. By understanding how to navigate and utilize Earth Null effectively, users can unlock a wealth of information that enhances their understanding of the planet.
We encourage you to explore Earth Null yourself and leave your thoughts in the comments below. If you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with others or checking out more of our content!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back on our site for more insightful articles!